Calculating Proportion In R - How to Calculate the Coefficient of Correlation : In other words, if you have a sample percentage of 5 percent, you must use 0.05 in the formula, not 5.
The r family effect sizes describe the proportion of variance that is explained by group membership e.g., a correlation (r) of 0.5 indicates 25% (r 2) of the variance is explained by the difference between groups. To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100. To begin, you must determine the value of the member's super interest. In other words, if you have a sample percentage of 5 percent, you must use 0.05 in the formula, not 5. Range from the attributable risk / the attributable risk) using the numbers from the examples presented so far, we have the following:
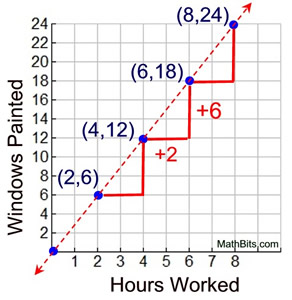
To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100.
When calculating a super benefit, you need to identify and calculate the value of the various components that make up the benefit. The r family effect sizes describe the proportion of variance that is explained by group membership e.g., a correlation (r) of 0.5 indicates 25% (r 2) of the variance is explained by the difference between groups. Range from the attributable risk / the attributable risk) using the numbers from the examples presented so far, we have the following: In other words, if you have a sample percentage of 5 percent, you must use 0.05 in the formula, not 5. These effect sizes are calculated from the sum of squares (the difference between individual observations and the mean for the. Since all assets are financed via equity or … To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100. The actual information in a data is the total variation it contains, remember?. This \(\chi^2\) statistic is obtained by calculating the difference between the observed number of cases and the. From the expected probits (yi), expected mortality proportion followed by expected no.of animals are derived. To begin, you must determine the value of the member's super interest.
These effect sizes are calculated from the sum of squares (the difference between individual observations and the mean for the. The r family effect sizes describe the proportion of variance that is explained by group membership e.g., a correlation (r) of 0.5 indicates 25% (r 2) of the variance is explained by the difference between groups. To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100. From the expected probits (yi), expected mortality proportion followed by expected no.of animals are derived. Since all assets are financed via equity or …
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TC_3126228-how-to-calculate-the-correlation-coefficient-5aabeb313de423003610ee40.png)
The r family effect sizes describe the proportion of variance that is explained by group membership e.g., a correlation (r) of 0.5 indicates 25% (r 2) of the variance is explained by the difference between groups.
Since all assets are financed via equity or … From the expected probits (yi), expected mortality proportion followed by expected no.of animals are derived. When calculating a super benefit, you need to identify and calculate the value of the various components that make up the benefit. These effect sizes are calculated from the sum of squares (the difference between individual observations and the mean for the. To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100. The actual information in a data is the total variation it contains, remember?. To begin, you must determine the value of the member's super interest. The r family effect sizes describe the proportion of variance that is explained by group membership e.g., a correlation (r) of 0.5 indicates 25% (r 2) of the variance is explained by the difference between groups. Range from the attributable risk / the attributable risk) using the numbers from the examples presented so far, we have the following: This \(\chi^2\) statistic is obtained by calculating the difference between the observed number of cases and the. In other words, if you have a sample percentage of 5 percent, you must use 0.05 in the formula, not 5.
This \(\chi^2\) statistic is obtained by calculating the difference between the observed number of cases and the. To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100. To begin, you must determine the value of the member's super interest. Range from the attributable risk / the attributable risk) using the numbers from the examples presented so far, we have the following: When calculating a super benefit, you need to identify and calculate the value of the various components that make up the benefit.

These effect sizes are calculated from the sum of squares (the difference between individual observations and the mean for the.
This \(\chi^2\) statistic is obtained by calculating the difference between the observed number of cases and the. From the expected probits (yi), expected mortality proportion followed by expected no.of animals are derived. When calculating a super benefit, you need to identify and calculate the value of the various components that make up the benefit. The actual information in a data is the total variation it contains, remember?. To begin, you must determine the value of the member's super interest. These effect sizes are calculated from the sum of squares (the difference between individual observations and the mean for the. Since all assets are financed via equity or … To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100. In other words, if you have a sample percentage of 5 percent, you must use 0.05 in the formula, not 5. Range from the attributable risk / the attributable risk) using the numbers from the examples presented so far, we have the following: The r family effect sizes describe the proportion of variance that is explained by group membership e.g., a correlation (r) of 0.5 indicates 25% (r 2) of the variance is explained by the difference between groups.
Calculating Proportion In R - How to Calculate the Coefficient of Correlation : In other words, if you have a sample percentage of 5 percent, you must use 0.05 in the formula, not 5.. These effect sizes are calculated from the sum of squares (the difference between individual observations and the mean for the. From the expected probits (yi), expected mortality proportion followed by expected no.of animals are derived. The r family effect sizes describe the proportion of variance that is explained by group membership e.g., a correlation (r) of 0.5 indicates 25% (r 2) of the variance is explained by the difference between groups. Since all assets are financed via equity or … To change a percentage into decimal form, simply divide by 100.
Post a Comment for "Calculating Proportion In R - How to Calculate the Coefficient of Correlation : In other words, if you have a sample percentage of 5 percent, you must use 0.05 in the formula, not 5."